Fallacy of Composition | Definition & Examples
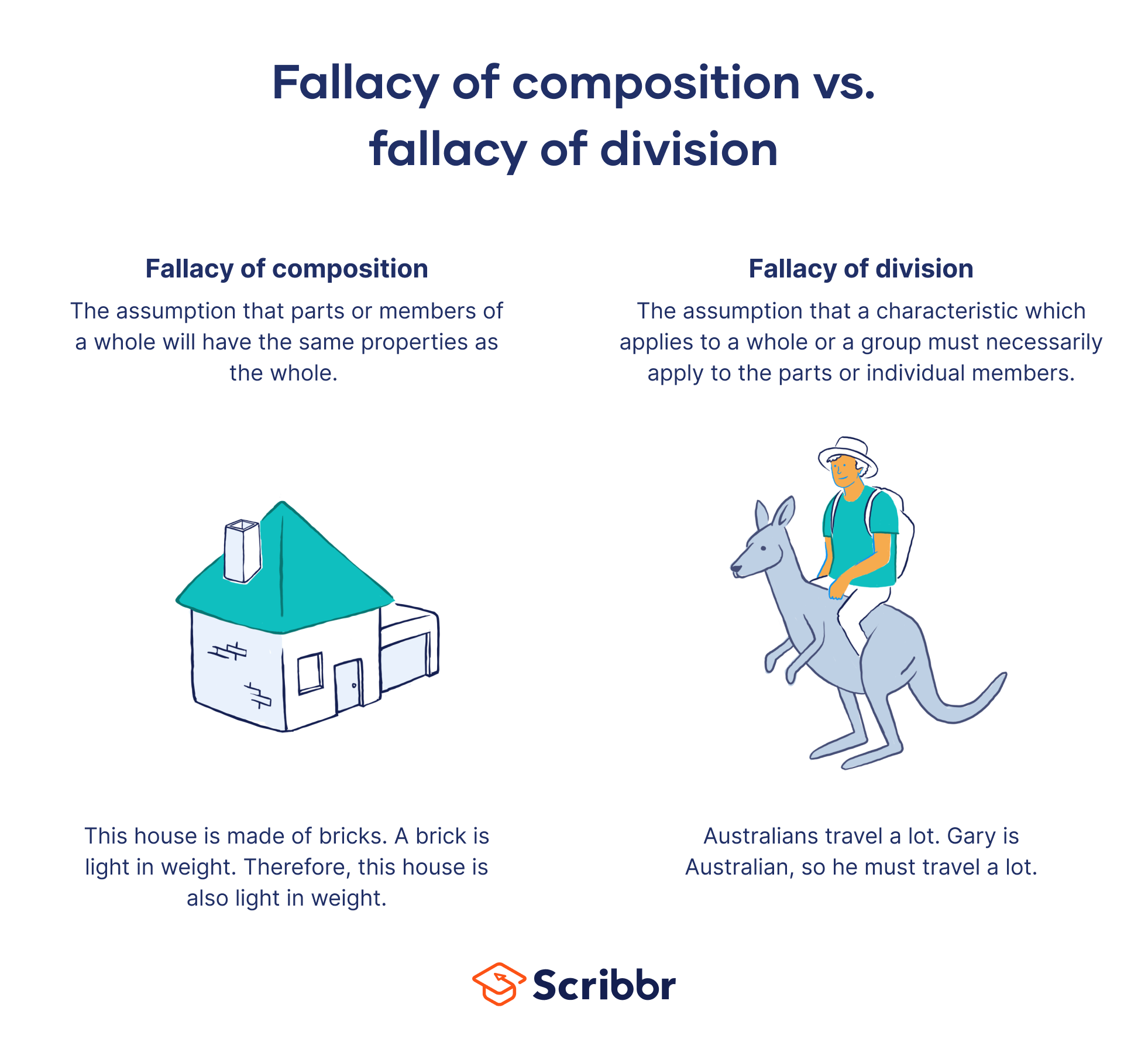
A fallacy of composition involves assuming that parts or members of a whole will have the same properties as the whole. This leads to wrong conclusions because what is true of the different parts is not necessarily true of the whole.
A fallacy of composition is an oversimplification that invalidates an argument.
What is the fallacy of composition?
The fallacy of composition is essentially the error of attributing to a group or a whole some characteristic that is true of its individual members (or parts).
Inferences based on this type of reasoning are considered to be fallacious because the collective (the group as a whole) and distributive (the members of a group) do not necessarily share the same properties. In other words, the mere fact that individuals have certain characteristics does not, in itself, guarantee that the class or group (taken as a whole) has those characteristics too.
The fallacy of composition is a logical fallacy or reasoning error. More specifically, it is an informal fallacy, meaning its error lies in the content of the argument, rather than the structure. Arguments of composition, as they are called, rest on the (implicit) premise that what is true of the parts of a whole is also true of the whole, without offering any justification.
How does the fallacy of composition work?
The fallacy of composition follows the general form:
- Y is part of X.
- Y has property A.
- Therefore, X also has property A.
The fallacy of composition can arise when we expect more (or less) from the whole than the individual parts can deliver. For example, the statement “All the players in the team are the best in their position, so this is the best team” is based on an erroneous assumption, because “the best team” is not necessarily an aggregation of the best players. Other factors play a role, like the ability to work together.
It is important to note that it may not always be wrong to infer that a whole has a certain property from the observation that all of its constituent parts have that property. The statement “All the parts of this desk are made of metal; therefore, this desk is made of metal” is clearly not fallacious.
The problem with fallacies of composition is not necessarily the move from the individual to the whole. Rather, it is the move from parts to whole in a context where an “emergent property” is being applied, (i.e., a property which a collection or complex system has, but which the individual parts do not have).
Because the emergent property depends upon interaction between parts, it cannot be found in the parts taken separately. For example, saltiness is a property of salt, but that does not mean that it is also a property of sodium and chlorine, the two elements which make up salt. The failure to realise that a property is emergent leads to the fallacy of composition.
How to identify a fallacy of composition
Recognising the fallacy of composition depends on our knowledge of the world and our ability to understand the parts-whole relationship in a given context. In the brick house example above, it’s easy to spot the fallacy because we know that a pile of bricks weighs more than a single brick. In other cases, it might be less obvious, so we need to ask ourselves the following questions:
- Is the characteristic being transferred from parts to a whole an absolute (e.g., green, square, acidic) or a relative property (e.g., small, rich, talk)? A house is green regardless of where it is located, while being rich involves an implicit comparison and depends on the context.
- What sort of whole or group is the characteristic being transferred into? If it’s transferred into a homogenous whole, then the argument is valid. For example, if a spoonful of soup is spicy, then we can safely conclude that the whole pot of soup is spicy.
- Does the aggregation of individual parts give rise to emergent properties? The way the parts interact with each other often changes the character of the whole. In this case, inferring something about the whole from the individual parts is fallacious. For example, human consciousness is considered an emergent property of the brain. The sum of all neurons in the nervous system generates complex human emotions like joy or fear, none of which can be attributed to a single neuron.
Fallacy of composition example
The “paradox of thrift” in economics is an example of the fallacy of composition.
Less demand means less consumption, less production, and fewer job opportunities. As a result, the recession will become worse and national wealth will be reduced.
The paradox of thrift happens because what is good or reasonable at the micro level of the economic behaviour of individuals can have devastating consequences at the macro level of a national economy.
Other interesting articles
If you want to know more about fallacies, research bias, or AI tools, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
AI tools
Fallacies
Frequently asked questions about the fallacy of composition
Sources for this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
This Scribbr articleNikolopoulou, K. (2023, October 30). Fallacy of Composition | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2025, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/fallacy/the-fallacy-of-composition/
Finocchiaro, M. A. (2015). The fallacy of composition: Guiding concepts, historical cases, and research problems. Journal of Applied Logic, 13(2), 24-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jal.2015.01.003