Parts of speech
- Can you start a sentence with a preposition?
-
Yes, it’s quite common to start a sentence with a preposition, and there’s no reason not to do so.
For example, the sentence “To many, she was a hero” is perfectly grammatical. It could also be rephrased as “She was a hero to many”, but there’s no particular reason to do so. Both versions are fine.
Some people argue that you shouldn’t end a sentence with a preposition, but that “rule” can also be ignored, since it’s not supported by serious language authorities.
- Can you end a sentence with a preposition?
-
Yes, it’s fine to end a sentence with a preposition. The “rule” against doing so is overwhelmingly rejected by modern style guides and language authorities and is based on the rules of Latin grammar, not English.
Trying to avoid ending a sentence with a preposition often results in very unnatural phrasings. For example, turning “He knows what he’s talking about” into “He knows about what he’s talking” or “He knows that about which he’s talking” is definitely not an improvement.
AI tools
- What kind of data are needed for deep learning?
-
Deep learning requires a large dataset (e.g., images or text) to learn from. The more diverse and representative the data, the better the model will learn to recognise objects or make predictions. Only when the training data is sufficiently varied can the model make accurate predictions or recognise objects from new data.
- Is using ChatGPT ethical?
-
ChatGPT and other AI writing tools can have unethical uses. These include:
- Reproducing biases and false information
- Using ChatGPT to cheat in academic contexts
- Violating the privacy of others by inputting personal information
However, when used correctly, AI writing tools can be helpful resources for improving your academic writing and research skills. Some ways to use ChatGPT ethically include:
- Following your institution’s guidelines
- Critically evaluating outputs
- Being transparent about how you used the tool
- Can ChatGPT write my college essay?
-
No, having ChatGPT write your college essay can negatively impact your application in numerous ways. ChatGPT outputs are unoriginal and lack personal insight.
Furthermore, Passing off AI-generated text as your own work is considered academically dishonest. AI detectors may be used to detect this offense, and it’s highly unlikely that any university will accept you if you are caught submitting an AI-generated admission essay.However, you can use ChatGPT to help write your college essay during the preparation and revision stages (e.g., for brainstorming ideas and generating feedback).
- Can ChatGPT feedback my college essay?
-
Yes, you use ChatGPT to help write your college essay by having it generate feedback on certain aspects of your work (consistency of tone, clarity of structure, etc.).
However, ChatGPT is not able to adequately judge qualities like vulnerability and authenticity. For this reason, it’s important to also ask for feedback from people who have experience with college essays and who know you well.
Alternatively, you can get advice using Scribbr’s essay editing service. - Can ChatGPT paraphrase text?
-
Yes, you can use ChatGPT to paraphrase text to help you express your ideas more clearly, explore different ways of phrasing your arguments, and avoid repetition.
However, it’s not specifically designed for this purpose. We recommend using a specialised tool like Scribbr’s free paraphrasing tool, which will provide a smoother user experience.
- Can ChatGPT summarise text?
-
Yes, you can use ChatGPT to summarise text. This can help you understand complex information more easily, summarise the central argument of your own paper, or clarify your research question.
You can also use Scribbr’s free text summariser, which is designed specifically for this purpose.
- What is knowledge representation and reasoning?
-
Knowledge representation and reasoning (KRR) is the study of how to represent information about the world in a form that can be used by a computer system to solve and reason about complex problems. It is an important field of artificial intelligence (AI) research.
An example of a KRR application is a semantic network, a way of grouping words or concepts by how closely related they are and formally defining the relationships between them so that a machine can “understand” language in something like the way people do.
A related concept is information extraction, concerned with how to get structured information from unstructured sources.
- What is information extraction?
-
Information extraction refers to the process of starting from unstructured sources (e.g., text documents written in ordinary English) and automatically extracting structured information (i.e., data in a clearly defined format that’s easily understood by computers). It’s an important concept in natural language processing (NLP).
For example, you might think of using news articles full of celebrity gossip to automatically create a database of the relationships between the celebrities mentioned (e.g., married, dating, divorced, feuding). You would end up with data in a structured format, something like MarriageBetween(celebrity1,celebrity2,date).
The challenge involves developing systems that can “understand” the text well enough to extract this kind of data from it.
- Is ChatGPT biased?
-
ChatGPT can sometimes reproduce biases from its training data, since it draws on the text it has “seen” to create plausible responses to your prompts.
For example, users have shown that it sometimes makes sexist assumptions such as that a doctor mentioned in a prompt must be a man rather than a woman. Some have also pointed out political bias in terms of which political figures the tool is willing to write positively or negatively about and which requests it refuses.
The tool is unlikely to be consistently biased toward a particular perspective or against a particular group. Rather, its responses are based on its training data and on the way you phrase your ChatGPT prompts. It’s sensitive to phrasing, so asking it the same question in different ways will result in quite different answers.
- Who owns the copyright of ChatGPT outputs?
-
According to OpenAI’s terms of use, users have the right to use outputs from their own ChatGPT conversations for any purpose (including commercial publication).
However, users should be aware of the potential legal implications of publishing ChatGPT outputs. ChatGPT responses are not always unique: different users may receive the same response.
Furthermore, ChatGPT outputs may contain copyrighted material. Users may be liable if they reproduce such material.
- Can I publish text written by ChatGPT?
-
According to OpenAI’s terms of use, users have the right to reproduce text generated by ChatGPT during conversations.
However, publishing ChatGPT outputs may have legal implications, such as copyright infringement.
Users should be aware of such issues and use ChatGPT outputs as a source of inspiration instead.
- How do I access ChatGPT?
-
You can access ChatGPT by signing up for a free account:
- Follow this link to the ChatGPT website.
- Click on “Sign up” and fill in the necessary details (or use your Google account). It’s free to sign up and use the tool.
- Type a prompt into the chat box to get started!
A ChatGPT app is also available for iOS, and an Android app is planned for the future. The app works similarly to the website, and you log in with the same account for both.
- Is ChatGPT free?
-
Yes, ChatGPT is currently available for free. You have to sign up for a free account to use the tool, and you should be aware that your data may be collected to train future versions of the model.
To sign up and use the tool for free, go to this page and click “Sign up”. You can do so with your email or with a Google account.
A premium version of the tool called ChatGPT Plus is available as a monthly subscription. It currently costs £16 and gets you access to features like GPT-4 (a more advanced version of the language model). But it’s optional: you can use the tool completely free if you’re not interested in the extra features.
- What are ChatGPT prompts?
-
ChatGPT prompts are the textual inputs (e.g., questions, instructions) that you enter into ChatGPT to get responses.
ChatGPT predicts an appropriate response to the prompt you entered. In general, a more specific and carefully worded prompt will get you better responses.
- What makes a good ChatGPT prompt?
-
A good ChatGPT prompt (i.e., one that will get you the kinds of responses you want):
- Gives the tool a role to explain what type of answer you expect from it
- Is precisely formulated and gives enough context
- Is free from bias
- Has been tested and improved by experimenting with the tool
- Can deep learning models be biased in their predictions?
-
Deep learning models can be biased in their predictions if the training data consist of biased information. For example, if a deep learning model used for screening job applicants has been trained with a dataset consisting primarily of white male applicants, it will consistently favour this specific population over others.
- Is ChatGPT a credible source?
-
No, ChatGPT is not a credible source of factual information and can’t be cited for this purpose in academic writing. While it tries to provide accurate answers, it often gets things wrong because its responses are based on patterns, not facts and data.
Specifically, the CRAAP test for evaluating sources includes five criteria: currency, relevance, authority, accuracy, and purpose. ChatGPT fails to meet at least three of them:
- Currency: The dataset that ChatGPT was trained on only extends to 2021, making it slightly outdated.
- Authority: It’s just a language model and is not considered a trustworthy source of factual information.
- Accuracy: It bases its responses on patterns rather than evidence and is unable to cite its sources.
So you shouldn’t cite ChatGPT as a trustworthy source for a factual claim. You might still cite ChatGPT for other reasons – for example, if you’re writing a paper about AI language models, ChatGPT responses are a relevant primary source.
- What is the best summariser tool?
-
Our research into the best summary generators (aka summarisers or summarising tools) found that the best summariser available in 2023 is the one offered by QuillBot.
While many summarisers just pick out some sentences from the text, QuillBot generates original summaries that are creative, clear, accurate, and concise. It can summarise texts of up to 1,200 words for free, or up to 6,000 with a premium subscription.
- How can I detect AI writing?
-
Tools called AI detectors are designed to label text as AI-generated or human. AI detectors work by looking for specific characteristics in the text, such as a low level of randomness in word choice and sentence length. These characteristics are typical of AI writing, allowing the detector to make a good guess at when text is AI-generated.
But these tools can’t guarantee 100% accuracy. Check out our comparison of the best AI detectors to learn more.
You can also manually watch for clues that a text is AI-generated – for example, a very different style from the writer’s usual voice or a generic, overly polite tone.
- How accurate are AI detectors?
-
AI detectors aim to identify the presence of AI-generated text (e.g., from ChatGPT) in a piece of writing, but they can’t do so with complete accuracy. In our comparison of the best AI detectors, we found that the 10 tools we tested had an average accuracy of 60%. The best free tool had 68% accuracy, the best premium tool 84%.
Because of how AI detectors work, they can never guarantee 100% accuracy, and there is always at least a small risk of false positives (human text being marked as AI-generated). Therefore, these tools should not be relied upon to provide absolute proof that a text is or isn’t AI-generated. Rather, they can provide a good indication in combination with other evidence.
- Can I use ChatGPT to learn languages?
-
Yes, there are a variety of ways to use ChatGPT for language learning, including treating it as a conversation partner, asking it for translations, and using it to generate a curriculum or practice exercises.
- Can I use ChatGPT as a conversation partner to learn a language?
-
Yes, using ChatGPT as a conversation partner is a great way to practice a language in an interactive way.
Try using a prompt like this one:
“Please be my Spanish conversation partner. Only speak to me in Spanish. Keep your answers short (maximum 50 words). Ask me questions. Let’s start the conversation with the following topic: [conversation topic].”
- Are ChatGPT conversations private?
-
ChatGPT conversations are generally used to train future models and to resolve issues/bugs. These chats may be monitored by human AI trainers.
However, users can opt out of having their conversations used for training. In these instances, chats are monitored only for potential abuse.
- Is there a ChatGPT app?
-
The official ChatGPT app is currently only available on iOS devices. If you don’t have an iOS device, only use the official OpenAI website to access the tool. This helps to eliminate the potential risk of downloading fraudulent or malicious software.
- Does ChatGPT store conversations?
-
OpenAI may store ChatGPT conversations for the purposes of future training. Additionally, these conversations may be monitored by human AI trainers.
Users can choose not to have their chat history saved. Unsaved chats are not used to train future models and are permanently deleted from ChatGPT’s system after 30 days.
- How does ChatGPT work?
-
ChatGPT is a chatbot based on a large language model (LLM). These models are trained on huge datasets consisting of hundreds of billions of words of text, based on which the model learns to effectively predict natural responses to the prompts you enter.
ChatGPT was also refined through a process called reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), which involves “rewarding” the model for providing useful answers and discouraging inappropriate answers – encouraging it to make fewer mistakes.
Essentially, ChatGPT’s answers are based on predicting the most likely responses to your inputs based on its training data, with a reward system on top of this to incentivise it to give you the most helpful answers possible. It’s a bit like an incredibly advanced version of predictive text. This is also one of ChatGPT’s limitations: because its answers are based on probabilities, they’re not always trustworthy.
- Who owns ChatGPT?
-
ChatGPT is owned by OpenAI, the company that developed and released it. OpenAI is a company dedicated to AI research. It started as a nonprofit company in 2015 but transitioned to for-profit in 2019. Its current CEO is Sam Altman, who also co-founded the company.
In terms of who owns the content generated by ChatGPT, OpenAI states that it will not claim copyright on this content, and the terms of use state that “you can use Content for any purpose, including commercial purposes such as sale or publication”. This means that you effectively own any content you generate with ChatGPT and can use it for your own purposes.
Be cautious about how you use ChatGPT content in an academic context. University policies on AI writing are still developing, so even if you “own” the content, you’re often not allowed to submit it as your own work according to your university or to publish it in a journal.
- Who created ChatGPT?
-
ChatGPT was created by OpenAI, an AI research company. It started as a nonprofit company in 2015 but became for-profit in 2019. Its CEO is Sam Altman, who also co-founded the company. OpenAI released ChatGPT as a free “research preview” in November 2022. Currently, it’s still available for free, although a more advanced premium version is available if you pay for it.
OpenAI is also known for developing DALL-E, an AI image generator that runs on similar technology to ChatGPT.
- What does “ChatGPT” stand for?
-
GPT stands for “generative pre-trained transformer”, which is a type of large language model: a neural network trained on a very large amount of text to produce convincing, human-like language outputs. The Chat part of the name just means “chat”: ChatGPT is a chatbot that you interact with by typing in text.
The technology behind ChatGPT is GPT-3.5 (in the free version) or GPT-4 (in the premium version). These are the names for the specific versions of the GPT model. GPT-4 is currently the most advanced model that OpenAI has created. It’s also the model used in Bing’s chatbot feature.
- Can I create citations using ChatGPT?
-
No, it is not possible to cite your sources with ChatGPT. You can ask it to create citations, but it isn’t designed for this task and tends to make up sources that don’t exist or present information in the wrong format. ChatGPT also cannot add citations to direct quotes in your text.
Instead, use a tool designed for this purpose, like the Scribbr Citation Generator.
But you can use ChatGPT for assignments in other ways, to provide inspiration, feedback, and general writing advice.
- Where does ChatGPT get its information from?
-
ChatGPT is an AI language model that was trained on a large body of text from a variety of sources (e.g., Wikipedia, books, news articles, scientific journals). The dataset only went up to 2021, meaning that it lacks information on more recent events.
It’s also important to understand that ChatGPT doesn’t access a database of facts to answer your questions. Instead, its responses are based on patterns that it saw in the training data.
So ChatGPT is not always trustworthy. It can usually answer general knowledge questions accurately, but it can easily give misleading answers on more specialist topics.
Another consequence of this way of generating responses is that ChatGPT usually can’t cite its sources accurately. It doesn’t really know what source it’s basing any specific claim on. It’s best to check any information you get from it against a credible source.
Text Summariser
- Can the summariser tool handle complex or technical language?
-
Yes, it can. The AI has been trained on a big dataset, so technical or complex data won’t be a problem for the text summariser.
- Can the summariser tool be used on mobile devices, or is it only available on desktop?
-
The text summariser is accessible on both desktop and mobile.
- How fast can the summariser tool generate a summary?
-
This text summariser can condense long text within seconds.
- How much text can the summariser tool handle at once?
-
At the moment, a maximum of 6,000 words can be summarised at once, within a few seconds. Want to summarise more? Just paste another block of text. There’s no limit on how much text you can summarise with our text summariser.
- Can the summariser make several versions of the same text, each with a different level of detail?
-
The text summariser can give you a longer or shorter summary, depending on your wishes. Want a more detailed summary? Just adjust the summary length at the top.
Paraphrasing Tool
- What’s the difference between paraphrasing, rephrasing, and rewording?
-
The act of putting someone else’s ideas or words into your own words is called paraphrasing, rephrasing, or rewording. Even though they are often used interchangeably, the terms can mean slightly different things:
Paraphrasing is restating someone else’s ideas or words in your own words while retaining their meaning. Paraphrasing changes sentence structure, word choice, and sentence length to convey the same meaning.
Rephrasing may involve more substantial changes to the original text, including changing the order of sentences or the overall structure of the text.
Rewording is changing individual words in a text without changing its meaning or structure, often using synonyms.
- Does the paraphrasing tool improve the readability and tone of the content?
-
It can. One of the two methods of paraphrasing is called “Fluency.” This will improve the language and fix grammatical errors in the text you’re paraphrasing.
- Is using a paraphrasing tool considered cheating?
-
Paraphrasing and using a paraphrasing tool aren’t cheating. It’s a great tool for saving time and coming up with new ways to express yourself in writing. However, always be sure to credit your sources. Avoid plagiarism.
- Why are references an important element in paraphrasing content?
-
If you don’t properly reference text paraphrased from another source, you’re plagiarising. If you use someone else’s text and paraphrase it, you need to credit the original source. You can do that by using citations. There are different styles, like APA, MLA, Harvard, and Chicago. Find more information about referencing sources here.
- Is paraphrasing considered plagiarism?
-
Paraphrasing without crediting the original author is a form of plagiarism, because you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
However, paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you correctly referencing the source. This means including an in-text citation and a full reference, formatted according to your required citation style.
As well as citing, make sure that any paraphrased text is completely rewritten in your own words.
- What is the difference between plagiarism and paraphrasing?
-
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words or ideas and passing them off as your own. Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas in your own words.
So when does paraphrasing count as plagiarism?
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if you don’t properly credit the original author.
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if your text is too close to the original wording (even if you cite the source). If you directly copy a sentence or phrase, you should quote it instead.
- Paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you put the author’s ideas completely in your own words and properly referencing the source.
Grammar Checker
- What’s the Scribbr Grammar Checker
-
The Scribbr Grammar Checker is a tailor-made AI-powered tool that can correct basic language, grammar, style, and spelling errors. We run it so that our editors are free to focus on what they do best: making sure that your paper is free of more nuanced mistakes and providing you with helpful feedback and writing tips.
The Scribbr Grammar Checker is a pro at correcting basic mistakes – and a human editor will still be carefully reviewing your full text – so you can rest assured that your paper is in very good hands!
When you receive back a document that has been reviewed by the Scribbr Grammar Checker, you’ll see two sets of tracked changes in it: one set from the grammar checker and one set from your editor. That way, you can easily tell who made what changes in your paper.
Not sure how tracked changes work in Word or how to review your edited file? Read our handy guide to learn more.
- What’s the best grammar checker?
-
We tested ten of the most popular free grammar checkers to see how many errors they could fix in our sample text and deducted points for any new errors introduced. We also evaluated the tools’ usability.
When compared all the other grammar checkers we tested for this comparison and Scribbr performed exceptionally well. It was successful in detecting and correcting 19 of the 20 errors. See the full review here.
- What can you do if the grammar checker finds an error that’s not really an error?
-
If our grammar checker flags an error that is not actually an error, you have several options:
1. Ignore the error: Most grammar checkers allow users to skip or ignore suggestions they do not agree with or find irrelevant. If you are confident that the flagged “error” is not an issue, you can bypass the suggestion and move on to the next one.
2. Review the context: Take a moment to thoroughly review the context surrounding the flagged error. Sometimes, the initial correct usage might still create confusion or ambiguity within the specific context, and reconsidering the phrasing could improve overall clarity.
- Does this grammar checker do more than fix grammar mistakes?
-
Yes, this grammar checker covers the following mistakes:
1. Grammar: Correction of grammatical errors such as subject-verb agreement, tense usage, and sentence structure
2. Spelling: identification and correction of spelling errors, including typos and commonly confused words.
3. Punctuation: Detection and rectification of punctuation errors, including incorrect use of commas, periods, colons, and other punctuation.
4. Word choice errors: Catch words that sound similar but aren’t, like their vs. they’re and your vs. you’re.
- Can I use this grammar checker for free?
-
Yes. There’s no sign up or payment required to use the grammar checker.
- Can I check my email, social media or any other communication to see if there are any grammar mistakes?
-
Yes. The grammar checker fixes any text, no matter what the medium is.
Spell Checker
- Is the spell checker free?
-
Yes, it is. It’s also completely ad-free, and no sign-up is required.
- Which languages does the spell checker support?
-
English, German, and French are supported. Because there are different English dialects worldwide, this spell checker supports UK, US, Canadian, and Australian English.
- How is this spell checker different from Word’s built-in spell checker?
-
Scribbr’s spell checker finds typos and misused words, unlike other spell checkers. It considers the context—the sentence’s subject and meaning—and the spelling and meaning of a word.
Punctuation Checker
- Does the punctuation checker also fix sentence structure?
-
Because this is an advanced punctuation checker, it also gives you suggestions for grammatically incorrect sentences.
- Is it cheating to use a punctuation checker when writing your paper?
-
It isn’t. Grammar checkers are acceptable in universities because they do not raise plagiarism concerns and aren’t considered unauthorized tools that provide an unfair advantage. Using a punctuation checker is just as legal as hiring a proofreader.
Methodology
- What is the definition of a hypothesis?
-
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research projects, you might have to write several hypotheses that address different aspects of your research question.
A hypothesis is not just a guess. It should be based on existing theories and knowledge. It also has to be testable, which means you can support or refute it through scientific research methods (such as experiments, observations, and statistical analysis of data).
- Why does data cleaning matter?
-
Data cleaning is necessary for valid and appropriate analyses. Dirty data contain inconsistencies or errors, but cleaning your data helps you minimise or resolve these.
Without data cleaning, you could end up with a Type I or II error in your conclusion. These types of erroneous conclusions can be practically significant with important consequences, because they lead to misplaced investments or missed opportunities.
- How do you randomly assign participants to a group?
-
To implement random assignment, assign a unique number to every member of your study’s sample.
Then, you can use a random number generator or a lottery method to randomly assign each number to a control or experimental group. You can also do so manually, by flipping a coin or rolling a die to randomly assign participants to groups.
- What’s the difference between correlation and causation?
-
Correlation describes an association between variables: when one variable changes, so does the other. A correlation is a statistical indicator of the relationship between variables.
Causation means that changes in one variable brings about changes in the other (i.e., there is a cause-and-effect relationship between variables). The two variables are correlated with each other, and there’s also a causal link between them.
While causation and correlation can exist simultaneously, correlation does not imply causation. In other words, correlation is simply a relationship where A relates to B—but A doesn’t necessarily cause B to happen (or vice versa). Mistaking correlation for causation is a common error and can lead to false cause fallacy.
AI tools
- What is the difference between classification and regression in supervised machine learning?
-
In classification, the goal is to assign input data to specific, predefined categories. The output in classification is typically a label or a class from a set of predefined options.
In regression, the goal is to establish a relationship between input variables and the output. The output in regression is a real-valued number that can vary within a range.
In both supervised learning approaches the goal is to find patterns or relationships in the input data so we can accurately predict the desired outcomes. The difference is that classification predicts categorical classes (like spam), while regression predicts continuous numerical values (like age, income, or temperature).
- How can I use ChatGPT for my term paper or bachelor thesis?
-
You can use ChatGPT to assist in the writing process for your research paper, thesis, or dissertation in the following ways:
- Why do we need algorithms?
-
Algorithms are valuable to us because they:
- Form the basis of much of the technology we use in our daily lives, from mobile apps to search engines.
- Power innovations in various industries that augment our abilities (e.g., AI assistants or medical diagnosis).
- Help analyse large volumes of data, discover patterns and make informed decisions in a fast and efficient way, at a scale humans are simply not able to do.
- Automate processes. By streamlining tasks, algorithms increase efficiency, reduce errors, and save valuable time.
- Are algorithms the same as computer programs?
-
Algorithms and computer programs are sometimes used interchangeably, but they refer to two distinct but interrelated concepts.
- An algorithm is a step-by-step instruction for solving a problem that is precise yet general.
- Computer programs are specific implementations of an algorithm in a specific programming language. In other words, the algorithm is the high-level description of an idea, while the program is the actual implementation of that idea.
- Are algorithms the same as artificial intelligence (AI)?
-
Algorithms and artificial intelligence (AI) are not the same, however they are closely related.
- Artificial intelligence is a broad term describing computer systems performing tasks usually associated with human intelligence like decision-making, pattern recognition, or learning from experience.
- Algorithms are the instructions that AI uses to carry out these tasks, therefore we could say that algorithms are the building blocks of AI – even though AI involves more advanced capabilities beyond just following instructions.
- What is an algorithm in computer science?
-
In computer science, an algorithm is a list of unambiguous instructions that specify successive steps to solve a problem or perform a task. Algorithms help computers execute tasks like playing games or sorting a list of numbers. In other words, computers use algorithms to understand what to do and give you the result you need.
- What is the exploration vs exploitation trade off in reinforcement learning?
-
A key challenge that arises in reinforcement learning (RL) is the trade-off between exploration and exploitation. This challenge is unique to RL and doesn’t arise in supervised or unsupervised learning.
Exploration is any action that lets the agent discover new features about the environment, while exploitation is capitalizing on knowledge already gained. If the agent continues to exploit only past experiences, it is likely to get stuck in a suboptimal policy. On the other hand, if it continues to explore without exploiting, it might never find a good policy.
An agent must find the right balance between the two so that it can discover the optimal policy that yields the maximum rewards.
- What is deep reinforcement learning?
-
Deep reinforcement learning is the combination of deep learning and reinforcement learning.
- Deep learning is a collection of techniques using artificial neural networks that mimic the structure of the human brain. With deep learning, computers can recognize complex patterns in large amounts of data, extract insights, or make predictions, without being explicitly programmed to do so. The training can consist of supervised learning, unsupervised learning, or reinforcement learning.
- Reinforcement learning (RL) is a learning mode in which a computer interacts with an environment, receives feedback and, based on that, adjusts its decision-making strategy.
- Deep reinforcement learning is a specialized form of RL that utilizes deep neural networks to solve more complex problems. In deep reinforcement learning, we combine the pattern recognition strengths of deep learning and neural networks with the feedback-based learning of RL.
- What are some real-life applications of reinforcement learning?
-
Some real-life applications of reinforcement learning include:
- Healthcare. Reinforcement learning can be used to create personalized treatment strategies, known as dynamic treatment regimes (DTRs), for patients with long-term illnesses. The input is a set of clinical observations and assessments of a patient. The outputs are the treatment options or drug dosages for every stage of the patient’s journey.
- Education. Reinforcement learning can be used to create personalized learning experiences for students. This includes tutoring systems that adapt to student needs, identify knowledge gaps, and suggest customized learning trajectories to enhance educational outcomes.
- Natural language processing (NLP). Text summarization, question answering, machine translation, and predictive text are all NLP applications using reinforcement learning.
- Robotics. Deep learning and reinforcement learning can be used to train robots that have the ability to grasp various objects , even objects they have never encountered before. This can, for example, be used in the context of an assembly line.
- How can I use AI writing tools?
-
AI writing tools can be used to perform a variety of tasks.
Generative AI writing tools (like ChatGPT) generate text based on human inputs and can be used for interactive learning, to provide feedback, or to generate research questions or outlines.
These tools can also be used to paraphrase or summarise text or to identify grammar and punctuation mistakes. You can also use Scribbr’s free paraphrasing tool, summarising tool, and grammar checker, which are designed specifically for these purposes.
- When should I use unsupervised learning?
-
Unsupervised learning should be used when your data is unlabeled and your goal is to discover the inherent structure or pattern in the data.
This approach is helpful for tasks like clustering, association, and dimensionality reduction.
- When should I use supervised learning?
-
Supervised learning should be used when your dataset consists of labeled data and your goal is to predict or classify new, unseen data based on the patterns learned from the labeled examples.
Tasks like image classification, sentiment analysis, and predictive modeling are common in supervised learning.
- What is generative art?
-
Generative art is art that has been created (generated) by some sort of autonomous system rather than directly by a human artist. Nowadays, the term is commonly used to refer to images created by generative AI tools like Midjourney and DALL-E. These tools use neural networks to create art automatically based on a prompt from the user (e.g., “an elephant painted in the style of Goya”).
However, the term has been in use since before this technology existed, and it can also refer to any technique use by an artist (or writer, musician, etc.) to create art according to a process that proceeds autonomously – i.e., outside of the artist’s direct control. Examples of generative art that does not involve AI include serialism in music and the cut-up technique in literature.
- What is an example of a machine learning application in real life?
-
A real-life application of machine learning is an email spam filter. To create such a filter, we would collect data consisting of various email messages and features (subject line, sender information, etc.) which we would label as spam or not spam. We would then train the model to recognize which features are associated with spam emails. In this way, the ML model would be able to classify any incoming emails as either unwanted or legitimate.
- What is the difference between machine learning and traditional programming?
-
Traditional programming and machine learning are essentially different approaches to problem-solving.
In traditional programming, a programmer manually provides specific instructions to the computer based on their understanding and analysis of the problem. If the data or the problem changes, the programmer needs to manually update the code.
In contrast, in machine learning the process is automated: we feed data to a computer and it comes up with a solution (i.e. a model) without being explicitly instructed on how to do this. Because the ML model learns by itself, it can handle new data or new scenarios.
Overall, traditional programming is a more fixed approach where the programmer designs the solution explicitly, while ML is a more flexible and adaptive approach where the ML model learns from data to generate a solution.
- Is artificial intelligence (AI) the same as machine learning (ML)?
-
Although the terms artificial intelligence and machine learning are often used interchangeably, they are distinct (but related) concepts:
- Artificial intelligence is a broad term that encompasses any process or technology aiming to build machines and computers that can perform complex tasks typically associated with human intelligence, like decision-making or translating.
- Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence that uses data and algorithms to teach computers how to learn and perform specific tasks without human interference.
In other words, machine learning is a specific approach or technique used to achieve the overarching goal of AI to build intelligent systems.
- What is the best summariser tool?
-
Our research into the best summary generators (aka summarisers or summarising tools) found that the best summariser available in 2023 is the one offered by QuillBot.
While many summarisers just pick out some sentences from the text, QuillBot generates original summaries that are creative, clear, accurate, and concise. It can summarise texts of up to 1,200 words for free, or up to 6,000 with a premium subscription.
KI-Text-Erkennung
- Does it detect content generated by ChatGPT, GPT4, or Gemini?
-
Scribbr’s AI Detectors can confidently detect most English texts generated by popular tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Copilot.
Our free AI detector can detect GPT2, GPT3, and GPT3.5 with average accuracy, while the Premium AI Detector has high accuracy and the ability to detect GPT4.
- How accurate is the AI detection software?
-
Our AI Detector can detect most texts generated by popular tools like ChatGPT and Bard. Unfortunately, we can’t guarantee 100% accuracy. The software works especially well with longer texts but can make mistakes if the AI output was prompted to be less predictable or was edited or paraphrased after being generated.
Our research into the best AI detectors indicates that no tool can provide complete accuracy; the highest accuracy we found was 84% in a premium tool or 68% in the best free tool.
- How do I interpret the AI score?
-
The AI score is a percentage between 0% and 100%, indicating the likelihood that a text has been generated by AI.
AI Detector
- Does it detect content generated by ChatGPT, GPT4, or Gemini?
-
Scribbr’s AI Detectors can confidently detect most English texts generated by popular tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Copilot.
Our free AI detector can detect GPT2, GPT3, and GPT3.5 with average accuracy, while the Premium AI Detector has high accuracy and the ability to detect GPT4.
- How accurate is the AI detection software?
-
Our AI Detector can detect most texts generated by popular tools like ChatGPT and Bard. Unfortunately, we can’t guarantee 100% accuracy. The software works especially well with longer texts but can make mistakes if the AI output was prompted to be less predictable or was edited or paraphrased after being generated.
Our research into the best AI detectors indicates that no tool can provide complete accuracy; the highest accuracy we found was 84% in a premium tool or 68% in the best free tool.
- How do I interpret the AI score?
-
The AI score is a percentage between 0% and 100%, indicating the likelihood that a text has been generated by AI.
Plagiarism Checker
- Can I buy a monthly subscription for the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker?
-
At the moment we do not offer a monthly subscription for the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker. Plagiarism checks can be bought separately — prices depend on the size of your document.
Small document (up to 7,499 words) £13.95 Normal document (7,500-49,999 words) £22.95 Large document (50,000+ words) £31.95 - Why are similarities marked in different colours?
-
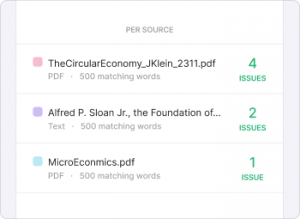
Similarities in your document are highlighted for quick and easy review. Each colour corresponds to a source in your Sources Overview at the right side of your report.
- I don’t recognize a source found by the plagiarism checker. What now?
-
Information can often be found in more than one place. For this reason, other sources citing the same information you used can come up in your Sources Overview.
The important thing is to make sure you’ve cited the source of the material. Try to find the original source, but if you can’t find it, it’s best to cite the source where you found the information.
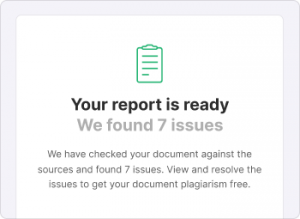
- What does a “high” or “moderate” risk of plagiarism mean?
-
Scribbr’s free plagiarism checker estimates the risk of plagiarism by calculating the percentage of text in your document that’s similar to other sources.
A moderate or high risk of plagiarism means that the plagiarism software detected several similarities worth reviewing.
Note that similarities are not necessarily plagiarism. You will need to decide on your own whether your text needs revision or citation.
- What is the difference between the free and premium report?
-
The free report tells you if your text contains potential plagiarism and other writing issues. The premium report gives you the resources you need to review issues in detail and resolve them.
Free report Premium report (from $19.95) Plagiarism Checker - Plagiarism risk assessment
- Top matching sources
Grammar Checker
- Number of writing issues
Plagiarism Checker - Precise similarity percentage
- Complete list of matching sources
- Document view to quickly review similarities
- Side-by-side comparison with the original text
- Upload private documents
Grammar Checker
- Downloadable Word document with all your writing issues corrected using Track Changes
AI Detector
- Precise AI writing percentage
- Can you use the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker for free?
-
Yes, Scribbr offers a limited free version of its plagiarism checker. It uses the industry-leading plagiarism detection technology and has access to most content databases.
- Should I check my paper for plagiarism before submitting it to my instructor?
-
If you’ve correctly cited all the sources you used, then you do not need to use a plagiarism checker before submitting your paper to your instructor. However, it is very easy to commit plagiarism accidentally, even if you’ve been very careful. To ensure that you didn’t forget to cite anything, you should use a plagiarism checker yourself.
A plagiarism checker works by using advanced database software to scan for matches between your text and existing texts.
To help you decide which checker to use, we conducted in-depth research comparing popular plagiarism checkers to find out which one is best.
- What is an acceptable percentage of plagiarism?
-
Your work should not contain any plagiarism. Even if your score is 1%, you will need to review each similarity and decide whether it’s necessary to revise your work.
But contrary to popular belief, plagiarism checkers work by detecting not plagiarism, but similarities. Not all similarities found by the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker constitute plagiarism. Our check sometimes flags the following:
- Properly cited quotes
- In-text citations or your reference list
- Commonly used phrases
- How accurate is Scribbr’s plagiarism checker?
-
Extensive testing proves that Scribbr’s plagiarism checker is one of the most accurate plagiarism checkers on the market in 2024.
The software detects everything from exact word matches to synonym swapping. It also has access to a full range of source types, including open- and restricted-access journal articles, theses and dissertations, websites, PDFs, and news articles.
- What languages are supported by the plagiarism checker?
-
Scribbr’s plagiarism checker offers complete support for 20 languages, including English, Spanish, German, Arabic, and Dutch. The add-on AI Detector is available for English, Spanish, German, French and Dutch texts.
The complete list of supported languages:
- Arabic
- Bosnian
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Finnish
- French
- German
- Greek
- Italian
- Norwegian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Russian
- Serbian
- Spanish
- Swedish
- Turkish
- What plagiarism and AI detection software does Scribbr use?
-
Scribbr uses advanced plagiarism detection technology similar to the software used by most universities and publishers in the UK, ensuring you receive the same or very similar results.
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software and is capable of detecting texts generated by ChatGPT, Perplexity and other generative AI tools with high accuracy.
- To which databases will my document be compared?
-
Your document will be compared to the world’s largest and fastest-growing content database, containing over:
- 99.3 billion current and historical webpages.
- 8 million publications from more than 1,700 publishers such as Springer, IEEE, Elsevier, Wiley-Blackwell, and Taylor & Francis.
- Can other plagiarism checkers see my submissions to Scribbr?
-
Your writing stays private. Your submissions to Scribbr are not published in any public database, so no other plagiarism checker (including those used by universities) will see them.
- Will Scribbr give the same result as my university’s plagiarism checker?
-
Scribbr uses similar plagiarism software to most universities in the UK, providing the same or very similar results.
However, universities may check your work against private student paper databases, which Scribbr can’t access, possibly leading to small differences.
To help, Scribbr offers a free Self-Plagiarism Checker add-on, allowing you to manually upload your source documents to ensure you haven’t accidentally plagiarized.
Self-Plagiarism Checker
- How can I compare two documents for plagiarism?
-
Most online plagiarism checkers only have access to public databases, whose software doesn’t allow you to compare two documents for plagiarism.
However, in addition to our Plagiarism Checker, Scribbr also offers an Self-Plagiarism Checker. This is an add-on tool that lets you compare your paper with unpublished or private documents. This way you can rest assured that you haven’t unintentionally plagiarised or self-plagiarised.
Compare two sources for plagiarism
- When should I use the Self-Plagiarism Checker instead of the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker?
-
The Scribbr Plagiarism Checker compares your document against the largest plagiarism database in the world. It will detect any similarities with documents in that database.
However, you might be unsure if all of the sources you used are in that database – for example, because some of your sources are unpublished. In this case, you can make use of our Self-Plagiarism Checker. Here you can add all the sources you want to a private database and compare them with your own document.
- How many sources can I add to the Self-Plagiarism Checker?
-
You can add up to 25 sources at a time to the Self-Plagiarism Checker. If you want to add more, you need to remove others first.
- How can I add internet sources?
-
Here’s how it works:
- Browse to your internet source and select the text. Right click and choose ‘Copy’.
- Head over to the Self-Plagiarism Checker and click the ‘Paste text’ button.
- Right click on the text area and choose paste.
- Your source text now appears in the text area.
- Click ‘Add source’ to upload your source.
- Will my sources/document be stored in a (shared) database?
-
No, the Self-Plagiarism Checker does not store your document in any public database.
In addition, you can delete all your personal information and documents from the Scribbr server as soon as you’ve received your plagiarism report.
- How can I download my Plagiarism Report?
-
Click the download icon at the bottom right of your screen.
- Which file formats can I upload as a source in the Self-Plagiarism Checker?
-
You can use the following file formats:
- .doc
- .docx
- .txt
If you have a document in a different file format, we recommend converting it to .docx or .pdf and then uploading it as a source.
- Can I change my original document?
-
No, it is not possible to change your original document. However, you can add, remove, and change as many sources as you want.
Reference Generator
- Is the Scribbr Reference Generator free?
-
Yes, the Scribbr APA Reference Generator is 100% free.
- Why should I use the Scribbr Reference Generator?
-
The Scribbr Reference Generator is easy to use, accurate, and accessible for all students. Some features you’ll definitely like include:
- Lightning-fast autocite using a URL, DOI, ISBN or title
- Smart citation forms that help you avoid incorrect citations
- Quick tips that make citing easier
- No costs, no ads, no limitations
- Can I download my sources to Word?
-
Yes, after creating your references you can download your reference list to Word. Simply click on download > Microsoft Word (.docx) in the menu above your reference list.
To save you some time, the downloaded file is already set up in APA format.
- What does a reference generator do?
-
A reference generator is an easy tool that helps you cite sources in a specific reference style.
You fill in the forms with information about a source, such as the author(s), title, and publication date. The tool then creates an accurate reference and in-text citation that you can use to give credit to the original author.
- Which citation software does Scribbr use?
-
The Scribbr Reference Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js. It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Reference Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github.
Citation Checker
- Does the APA Citation Checker check my reference entries?
-
Reference entries are cross-checked with in-text citations to make sure there are no inconsistencies or missing entries. However, the APA Citation Checker does not check the contents or formatting of the reference entries themselves.
- Which languages are supported?
-
The APA Citation Checker can check documents in the following languages:
- English
- Spanish
- German
- French
- Dutch
- Which citation styles are supported?
-
The APA Citation Checker currently supports APA Style 6th edition (2009) and 7th edition (2020). We are working hard to support more citation styles in the future.
Need help with a different citation style? Check out Scribbr’s Citation Editing Service.
- Can I check my document multiple times?
-
Yes. After fixing your citations, you can upload your revised document and perform a second check free of charge. This way, you can rest assured that you haven’t introduced any new mistakes.
- What’s the difference between the APA Citation Checker and Citation Editing?
-
The APA Citation Checker is an automated tool that helps you detect and resolve issues with your in-text citations. Citation Editing is performed by human citation experts who will edit your in-text citations and reference entries.
Proofreading & Editing
- How can I contact Scribbr?
-
Our support team is here to help you daily via chat, WhatsApp, email, or phone between 9:00 a.m. to 11:00 p.m. CET.
- Can I choose between the 6th and 7th editions of APA Style?
-
Our APA experts default to APA 7 for editing and formatting. For the Citation Editing Service you are able to choose between APA 6 and 7.
- Can I get a sample edit?
-
Yes, if your document is longer than 20,000 words, you will get a sample of approximately 2,000 words. This sample edit gives you a first impression of the editor’s editing style and a chance to ask questions and give feedback.
How does the sample edit work?
You will receive the sample edit within 24 hours after placing your order. You then have 24 hours to let us know if you’re happy with the sample or if there’s something you would like the editor to do differently.
- Can I upload my document in sections?
-
Yes, you can upload your document in sections.
We try our best to ensure that the same editor checks all the different sections of your document. When you upload a new file, our system recognizes you as a returning customer, and we immediately contact the editor who helped you before.
However, we cannot guarantee that the same editor will be available. Your chances are higher if
- You send us your text as soon as possible and
- You can be flexible about the deadline.
Please note that the shorter your deadline is, the lower the chance that your previous editor is not available.
If your previous editor isn’t available, then we will inform you immediately and look for another qualified editor. Fear not! Every Scribbr editor follows the Scribbr Improvement Model and will deliver high-quality work.
- Can I have my document edited during weekends and holidays?
-
Yes, our editors also work during the weekends and holidays.
Because we have many editors available, we can check your document 24 hours per day and 7 days per week, all year round.
If you choose a 72 hour deadline and upload your document on a Thursday evening, you’ll have your thesis back by Sunday evening!
- English is not my first language. Can you fix all my mistakes?
-
Yes! Our editors are all native speakers, and they have lots of experience editing texts written by ESL students. They will make sure your grammar is perfect and point out any sentences that are difficult to understand. They’ll also notice your most common mistakes, and give you personal feedback to improve your writing in English.
- What types of editing does Scribbr offer?
-
Every Scribbr order comes with our award-winning Proofreading & Editing service, which combines two important stages of the revision process.
For a more comprehensive edit, you can add a Structure Check or Clarity Check to your order. With these building blocks, you can customize the kind of feedback you receive.
You might be familiar with a different set of editing terms. To help you understand what you can expect at Scribbr, we created this table:
Types of editing Available at Scribbr? Proofreading
Correction of superficial mistakes, such as typos, misspellings, punctuation errors and consistency errors.Yes!
This is the “proofreading” in Scribbr’s standard service. It can only be selected in combination with editing.Copy editing
Focus on grammar, syntax, style, tone and the conventions of the field. The editor also considers the internal logic of the text and flags any obvious contradictions.Yes!
This is the “editing” in Scribbr’s standard service. It can only be selected in combination with proofreading.Line editing
Focus on language, style, concision and choices. The editor helps you strengthen your story, polish your sentences and ensure that your use of language drives home your ideas.Yes!
Select the Structure Check and Clarity Check to receive a comprehensive edit equivalent to a line edit.Developmental editing (i.e. content editing, substantive editing)
This is the first step of the editing process and applies to very early drafts. The editor helps you structure your ideas, decide what story to tell and find direction for your writing.No.
This kind of editing involves heavy rewriting and restructuring. Our editors cannot help with this. - Is the editor an expert in my field of study?
-
When you place an order, you can specify your field of study and we’ll match you with an editor who has familiarity with this area.
However, our editors are language specialists, not academic experts in your field. Your editor’s job is not to comment on the content of your dissertation, but to improve your language and help you express your ideas as clearly and fluently as possible.
This means that your editor will understand your text well enough to give feedback on its clarity, logic and structure, but not on the accuracy or originality of its content.
Good academic writing should be understandable to a non-expert reader, and we believe that academic editing is a discipline in itself. The research, ideas and arguments are all yours – we’re here to make sure they shine!
- How do I receive my document when the editor has finished proofreading?
-
After your document has been edited, you will receive an email with a link to download the document.
The editor has made changes to your document using ‘Track Changes’ in Word. This means that you only have to accept or ignore the changes that are made in the text one by one.
It is also possible to accept all changes at once. However, we strongly advise you not to do so for the following reasons:
- You can learn a lot by looking at the mistakes you made.
- The editors don’t only change the text – they also place comments when sentences or sometimes even entire paragraphs are unclear. You should read through these comments and take into account your editor’s tips and suggestions.
- With a final read-through, you can make sure you’re 100% happy with your text before you submit!
- I have a tight deadline. Can you edit my document in time?
-
You choose the turnaround time when ordering. We can return your dissertation within 24 hours, 3 days or 1 week. These timescales include weekends and holidays. As soon as you’ve paid, the deadline is set, and we guarantee to meet it! We’ll notify you by text and email when your editor has completed the job.
Very large orders might not be possible to complete in 24 hours. On average, our editors can complete around 13,000 words in a day while maintaining our high quality standards. If your order is longer than this and urgent, contact us to discuss possibilities.
Always leave yourself enough time to check through the document and accept the changes before your submission deadline.
- What type of documents does Scribbr proofread?
-
Scribbr is specialised in editing study related documents. We check:
- PhD Theses
- Graduation projects
- Dissertations
- Essays
- Admissions essays
- College essays
- Application essays
- Personal statements
- Reports
- Process reports
- Reflections
- Internship reports
- Academic papers
- Interviews
- Proposals
- Research proposals
- Prospectuses
- How fast can Scribbr proofread my document?
-
The fastest turnaround time is 24 hours.
You can upload your document at any time and choose between four deadlines:
- Same day delivery
- 3 hours
- 6 hours
- 12 hours
- 24 hours
- 3 days
- 7 days
- Same day delivery
- What is Scribbr’s 100% happiness guarantee?
-
At Scribbr, we promise to make every customer 100% happy with the service we offer. Our philosophy: Your complaint is always justified – no denial, no doubts.
Our customer support team is here to find the solution that helps you the most, whether that’s a free new edit or a refund for the service.
- Can I choose between American, British and Australian English?
-
Yes, in the order process you can indicate your preference for American, British, or Australian English.
If you don’t choose one, your editor will follow the style of English you currently use. If your editor has any questions about this, we will contact you.

 Click the download icon at the bottom right of your screen.
Click the download icon at the bottom right of your screen.