Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples
In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different treatment groups using randomisation.
With simple random assignment, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control group or an experimental group. Studies that use simple random assignment are also called completely randomised designs.
Random assignment is a key part of experimental design. It helps you ensure that all groups are comparable at the start of a study: any differences between them are due to random factors.
Why does random assignment matter?
Random assignment is an important part of control in experimental research, because it helps strengthen the internal validity of an experiment.
In experiments, researchers manipulate an independent variable to assess its effect on a dependent variable, while controlling for other variables. To do so, they often use different levels of an independent variable for different groups of participants.
This is called a between-groups or independent measures design.
You use three groups of participants that are each given a different level of the independent variable:
- A control group that’s given a placebo (no dosage)
- An experimental group that’s given a low dosage
- A second experimental group that’s given a high dosage
Random assignment to helps you make sure that the treatment groups don’t differ in systematic or biased ways at the start of the experiment.
If you don’t use random assignment, you may not be able to rule out alternative explanations for your results.
- Participants recruited from pubs are placed in the control group
- Participants recruited from local community centres are placed in the low-dosage experimental group
- Participants recruited from gyms are placed in the high-dosage group
With this type of assignment, it’s hard to tell whether the participant characteristics are the same across all groups at the start of the study. Gym users may tend to engage in more healthy behaviours than people who frequent pubs or community centres, and this would introduce a healthy user bias in your study.
If your study outcomes show more energy in the high-dosage group, you might not be able to attribute this result solely to your independent variable manipulation (the iron supplement). Instead, this result may come from the interaction between the participants’ characteristics and the independent variable.
Although random assignment helps even out baseline differences between groups, it doesn’t always make them completely equivalent. There may still be extraneous variables that differ between groups, and there will always be some group differences that arise from chance.
Most of the time, the random variation between groups is low, and, therefore, it’s acceptable for further analysis. This is especially true when you have a large sample. In general, you should always use random assignment in experiments when it is ethically possible and makes sense for your study topic.
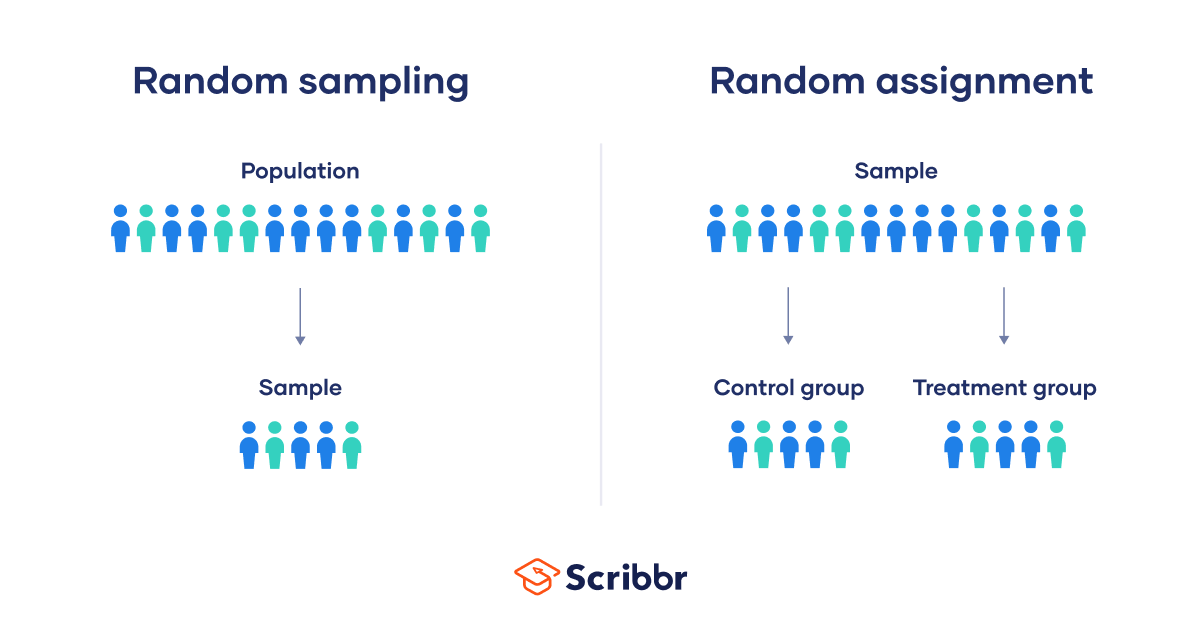
Random sampling vs random assignment
Random sampling and random assignment are both important concepts in research, but it’s important to understand the difference between them.
Random sampling (also called probability sampling or random selection) is a way of selecting members of a population to be included in your study. In contrast, random assignment is a way of sorting the sample participants into control and experimental groups.
While random sampling is used in many types of studies, random assignment is only used in between-subjects experimental designs.
Some studies use both random sampling and random assignment, while others use only one or the other.
Random sampling enhances the external validity or generalisability of your results, because it helps to ensure that your sample is unbiased and representative of the whole population. This allows you to make stronger statistical inferences.
You use a simple random sample to collect data. Because you have access to the whole population (all employees), you can assign all 8,000 employees a number and use a random number generator to select 300 employees. These 300 employees are your full sample.
By using a random sample, you can be reasonably confident that your results are applicable across the whole company.
Random assignment enhances the internal validity of the study, because it ensures that there are no systematic differences between the participants in each group. This helps you conclude that the outcomes can be attributed to the independent variable.
- A control group that receives no intervention
- An experimental group that has a remote team-building intervention every week for a month
You use random assignment to place participants into the control or experimental group. To do so, you take your list of participants and assign each participant a number. Again, you use a random number generator to place each participant in one of the two groups.
By using random assignment, you can be reasonably confident that any differences in employee engagement outcomes are an effect of the team-building intervention (and not caused by other differences between the groups).
How do you use random assignment?
To use simple random assignment, you start by giving every member of the sample a unique number. Then, you can use computer programs or manual methods to randomly assign each participant to a group.
- Random number generator: Use a computer program to generate random numbers from the list for each group.
- Lottery method: Place all numbers individually into a hat or a bucket, and draw numbers at random for each group.
- Flip a coin: When you only have two groups, for each number on the list, flip a coin to decide if they’ll be in the control or the experimental group.
- Use a dice: When you have three groups, for each number on the list, roll a die to decide which of the groups they will be in. For example, assume that rolling 1 or 2 lands them in a control group; 3 or 4 in an experimental group; and 5 or 6 in a second control or experimental group.
This type of random assignment is the most powerful method of placing participants in conditions, because each individual has an equal chance of being placed in any one of your treatment groups.
Random assignment in block designs
In more complicated experimental designs, random assignment is only used after participants are grouped into blocks based on some characteristic (e.g., test score or demographic variable). These groupings mean that you need a larger sample to achieve high statistical power.
For example, a randomised block design involves placing participants into blocks based on a shared characteristic (e.g., college students vs graduates), and then using random assignment within each block to assign participants to every treatment condition. This helps you assess whether the characteristic affects the outcomes of your treatment.
In an experimental matched design, you use blocking and then match up individual participants from each block based on specific characteristics. Within each matched pair or group, you randomly assign each participant to one of the conditions in the experiment and compare their outcomes.
When is random assignment not used?
Sometimes, it’s not relevant or ethical to use simple random assignment, so groups are assigned in a different way.
When comparing different groups
Sometimes, differences between participants are the main focus of a study, for example, when comparing children and adults or people with and without health conditions. Participants are not randomly assigned to different groups, but instead assigned based on their characteristics.
In this type of study, the characteristic of interest (e.g., gender) is an independent variable, and the groups differ based on the different levels (e.g., men, women). All participants are tested the same way, and then their group-level outcomes are compared.
When it’s not ethically permissible
When studying unhealthy or dangerous behaviours, it’s not possible to use random assignment. For example, if you’re studying heavy drinkers and social drinkers, it’s unethical to randomly assign participants to one of the two groups and ask them to drink large amounts of alcohol for your experiment.
When you can’t assign participants to groups, you can also conduct a quasi-experimental study. In a quasi-experiment, you study the outcomes of pre-existing groups who receive treatments that you may not have any control over (e.g., heavy drinkers and social drinkers).
These groups aren’t randomly assigned, but may be considered comparable when some other variables (e.g., age or socioeconomic status) are controlled for.
Frequently asked questions about random assignment
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, February 13). Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 15 December 2025, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/random-assignment-experiments/